Like women, men can also have abnormal BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. The lifetime risk of men developing breast cancer is about 1 in 1000.
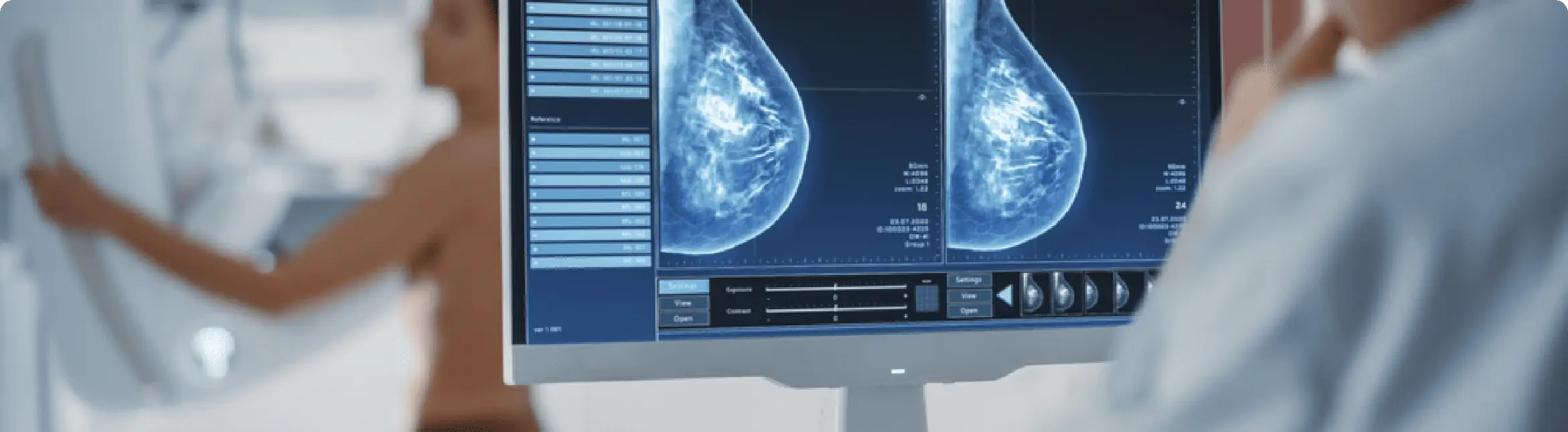
About 5% – 10% of breast cancers are hereditary (caused by abnormal genes passed from a parent to their child). Most of these are due to the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. It is important to know that mutations in these genes are also associated with some other kinds of cancers, including ovarian cancer, colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer and melanoma.
Men with BRCA1 mutations have a slightly increased risk of breast and prostate cancer. Those with BRCA2 gene mutations are 8 times more likely to develop breast cancer and 7 times more likely to develop prostate cancer.
You can reduce the risk of developing these cancers with regular screening, health diet and exercise, moderating alcohol intake and not smoking.
If you have, or suspect you have a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer, then you should speak to you general practitioner who can organise the appropriate tests and refer you on for a specialist opinion.